What is the difference Between Hardened Connectivity vs. Non-Hardened Connectivity?
Hardened connectivity refers to fiber-optic network components designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions. These components, including connectors and terminals, are built with protective materials that shield them from extreme temperatures, moisture, UV radiation, and physical stress.
Definition of Non-Hardened Connectivity
Non-hardened connectivity consists of standard fiber-optic components that are typically used in controlled environments, such as indoor data centers or protected enclosures. These components lack the additional protective features found in hardened solutions and may require extra precautions for outdoor deployment.
Key Differences in Design and Durability
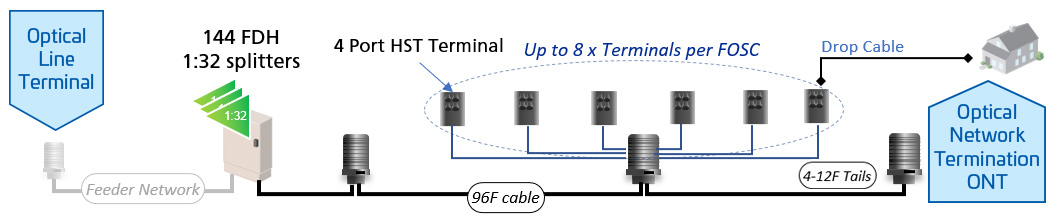
Hardened connectivity solutions are factory-sealed and environmentally protected, allowing them to be deployed in aerial, underground, and outdoor applications without additional housing. Non-hardened connectivity, on the other hand, often requires protective enclosures or specialized installation techniques to maintain performance in challenging conditions.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Hardened connectivity enables plug-and-play installation, reducing the need for fiber splicing and minimizing labor costs. These solutions simplify network expansion and maintenance by eliminating the need for re-entry into terminals. Non-hardened connectivity may involve more complex installation processes, including splicing and additional protective measures.
Applications in Network Infrastructure
Hardened connectivity is widely used in fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) and outside plant (OSP) deployments, where reliability and durability are critical. Non-hardened connectivity is more common in indoor enterprise networks and data center environments, where environmental exposure is minimal.
Related CommScope Links: